Scratch-resistant glass in smartphones is a special type of protective material designed to withstand damage from daily wear and tear. Typically made from chemically strengthened materials like Alkali aluminosilicate, this glass is treated to enhance its durability and resistance to scratches and cracks. By using an advanced manufacturing process, companies like Corning Inc. have developed versions of Gorilla Glass that not only protect your screen from accidental scratches but also maintain optical clarity and touch sensitivity. This innovation has become a crucial feature for smartphone users who want their devices to look good and perform well, even after extended use.
Types of Scratch-Resistant Glass
1. Gorilla Glass
Gorilla Glass, developed by Corning Inc., is perhaps the most widely recognized name when it comes to scratch-resistant glass for smartphones. First introduced in 2007, it gained popularity due to its combination of toughness and thinness. The glass undergoes a process called ion exchange, where the glass is immersed in a molten potassium salt bath. This allows larger potassium ions to replace smaller sodium ions, creating a layer of compression on the surface that makes it more resistant to scratches and impacts. Over the years, Corning has released multiple versions of Gorilla Glass, each improving on durability, scratch resistance, and drop protection. For instance, Gorilla Glass Victus offers twice the scratch resistance of previous versions and can survive drops from up to two meters, making it ideal for those prone to occsional mishaps.
2. Dragontrail Glass
Dragontrail Glass, manufactured by Asahi Glass Co. (AGC), is another strong contender in the world of tough smartphone glass. Similar to Gorilla Glass, it is chemically treated to enhance its scratch and shatter resistance. It was first introduced as a direct competitor to Corning’s product, offering a similar level of durability while also being cost-effective. Dragontrail Glass is often used in rugged phones designed to withstand harsh conditions, as well as in mid-range smartphones looking for a balance of quality and price. The glass is designed to handle the everyday wear and tear that smartphones face, including scratches from keys or coins, and accidental drops.
3. Sapphire Glass
Sapphire glass is made from synthetic sapphire, which is an incredibly hard material just below diamond in terms of hardness on the Mohs scale. This property makes it extremely scratch-resistant; only materials harder than sapphire, like diamonds, can scratch it. While sapphire glass is exceptionally tough, it is also more expensive to manufacture compared to other types of glass. For this reason, it is typically reserved for high-end smartphones and luxury devices. Some smartphone manufacturers, like Apple, have used sapphire glass for specific components, such as camera lenses and fingerprint sensors, to prevent scratches from affecting their performance. Its high hardness, however, also makes it more brittle, which means it can shatter upon impact more easily than other materials.
4. Tempered Glass
Tempered glass is made by heating the glass to a high temperature and then rapidly cooling it, a process that increases its strength and makes it more resistant to breaking. While it doesn’t offer the same level of scratch resistance as chemically treated glasses like Gorilla or Dragontrail, tempered glass is still effective in protecting screens from impacts and shattering. This type of glass is also commonly used in screen protectors, which can be easily replaced if scratched or cracked. It’s a more affordable option for those looking to add a layer of protection to their devices without opting for a more advanced, built-in glass.
5. Plastic Glass (Polycarbonate)
Plastic glass, also known as polycarbonate, is not technically glass but is used in some devices as a protective layer. It is lightweight, shatter-resistant, and highly flexible, which makes it a popular choice for rugged devices and budget-friendly smartphones. Unlike traditional glass, polycarbonate can absorb more impacts without cracking, but it is also more prone to scratches. To mitigate this, some manufacturers apply scratch-resistant coatings on polycarbonate screens. However, even with such coatings, polycarbonate is generally less scratch-resistant compared to other materials like Gorilla Glass or sapphire glass.
6. Ceramic Shield
Ceramic Shield is a technology introduced by Apple with the iPhone 12. This innovation involves infusing nano-ceramic crystals directly into the glass, making it tougher and more resistant to drops and scratches. The ceramic crystals, while incredibly hard, remain transparent, preserving the clarity of the screen. Apple claims that this makes Ceramic Shield four times more resistant to damage from drops compared to previous iPhone models. This balance of toughness and optical clarity allows users to have a screen that is not only durable but also delivers a vibrant and clear viewing experience. Ceramic Shield represents a step forward in scratch-resistant technology, combining the strength of ceramics with the flexibility of glass.
 Development and Evolution of Scratch-Resistant Glass
Development and Evolution of Scratch-Resistant Glass
Over the years, various companies have contributed to this evolution by developing new technologies and refining existing ones, resulting in a wide range of products tailored for different types of devices. Let’s explore the key milestones in the development and evolution of scratch-resistant glass:
1. Chemcor Glass (1960s)
The roots of scratch-resistant glass can be traced back to Corning’s Chemcor project in the 1960s. Originally developed for industrial use, Chemcor glass was strong and durable but was not widely adopted due to limited applications. This early experimentation laid the foundation for future developments, showing Corning the potential of chemically strengthened glass.
2. Introduction of Gorilla Glass (2007)
The real breakthrough came in 2007 when Corning launched the first version of Gorilla Glass. It was specially designed for the original iPhone, combining strength with a thin profile to create a protective layer that did not compromise the sleek design of the device. Its success led to widespread adoption by other smartphone manufacturers, marking the beginning of a new era for scratch-resistant screens.
3. Gorilla Glass 2 (2012)
In 2012, Corning introduced Gorilla Glass 2, which maintained the same durability as the original but was 20% thinner. This allowed manufacturers to design slimmer, lighter devices without sacrificing screen protection. It was a significant step forward in creating more compact and aesthetically pleasing smartphones.
4. Gorilla Glass 3 with Native Damage Resistance (2013)
The third generation brought in a new feature called Native Damage Resistance (NDR), which improved the glass’s ability to handle deeper scratches without affecting its structure. This innovation made the glass tougher and more flexible, setting a new standard for screen protection in smartphones and tablets.
5. Gorilla Glass 4 Focus on Drop Resistance (2014)
In response to consumer concerns about screen breakage from drops, Corning developed Gorilla Glass 4, which focused on enhancing drop resistance. According to lab tests, it could survive falls from a height of one meter 80% of the time, offering users peace of mind when handling their devices.
6. Introduction of Sapphire Glass (2014)
Around the same time, sapphire glass gained attention as a potential alternative to Gorilla Glass. Known for its extreme hardness and scratch resistance, sapphire glass was used in some high-end devices. However, due to high production costs and brittleness, it did not become a mainstream choice for smartphone screens but found its place in smaller components like camera lenses and smartwatch displays.
7. Gorilla Glass 5 and Enhanced Drop Protection (2016)
With Gorilla Glass 5, Corning further improved drop resistance, making the glass four times more resilient than its predecessor. It was designed to survive drops from a height of 1.6 meters, a common scenario for people taking selfies or using their phones at head height. This version continued to solidify Gorilla Glass’s reputation for durability.
8. Gorilla Glass 6 and the Rise of Scratch-Resistant Wearables (2018)
Launched in 2018, Gorilla Glass 6 could withstand up to 15 consecutive drops from a one-meter height onto hard surfaces. This version also marked the expansion of Corning’s technology into wearables, with specialized versions like Gorilla Glass SR+ designed to offer the same scratch resistance for smartwatches and fitness trackers.
9. Ceramic Shield (2020)
Apple’s Ceramic Shield, introduced with the iPhone 12, represented a major innovation. By infusing ceramic crystals into the glass, Apple was able to significantly improve both scratch resistance and drop performance. This technology offered a new way to enhance screen protection without compromising clarity or touch sensitivity.
10. Gorilla Glass Victus (2020)
Corning launched Gorilla Glass Victus, which set new records for both scratch and drop resistance. Capable of surviving drops from two meters and offering twice the scratch resistance of Gorilla Glass 6, Victus was a significant upgrade and was quickly adopted by many leading smartphone brands.
11. Gorilla Glass 7i and Victus 2 (2023-2024)
The latest advancements, Gorilla Glass 7i and Victus 2, have continued to build on Corning’s legacy of toughness and innovation. Victus 2 focuses on surviving drops on rougher surfaces like concrete and asphalt, while Gorilla Glass 7i is designed to offer an affordable yet tough option for mid-range smartphones. These versions ensure that even budget-conscious consumers can benefit from durable and scratch-resistant screens.
 Key Properties and Benefits of Scratch-Resistant Glass
Key Properties and Benefits of Scratch-Resistant Glass
Scratch-resistant glass has become a standard feature in modern smartphones, offering users a blend of durability, functionality, and aesthetic appeal. Designed to endure the daily wear and tear of constant use, this type of glass is chemically strengthened to resist scratches, impacts, and other forms of damage. Its unique properties make it an essential component for electronic devices, ensuring that screens remain clear and responsive over time. Here are the key properties and benefits of scratch-resistant glass:
1. High Scratch Resistance
The most prominent feature of scratch-resistant glass is its ability to withstand scratches from everyday objects like keys, coins, and even rough surfaces. This is achieved through chemical strengthening processes, such as ion exchange, which create a tough, compressed surface layer. This property ensures that your smartphone screen remains clear and scratch-free, even after prolonged use.
2. Enhanced Durability and Impact Resistance
Scratch-resistant glass is not just about preventing scratches; it’s also designed to be more durable overall. This glass can withstand drops and bumps better than regular glass, reducing the chances of screen cracks and shattering. For example, versions like Gorilla Glass Victus can survive multiple drops from a height of up to two meters, making it ideal for active users who need their devices to endure rough handling.
3. Thin and Lightweight Design
One of the impressive properties of scratch-resistant glass is its ability to remain thin and lightweight without compromising strength. This allows manufacturers to design sleek, slim devices that are easy to carry and use. Despite its thin profile, the glass offers robust protection, ensuring that your device remains both stylish and durable.
4. Excellent Optical Clarity
Scratch-resistant glass is engineered to maintain high optical clarity, providing users with bright, vivid displays. This is particularly important for smartphones, where screen quality affects everything from reading text to watching videos. Advanced glass technology ensures that there is minimal distortion, allowing for a crystal-clear viewing experience.
5. Improved Touch Sensitivity
Besides being tough, scratch-resistant glass is also designed to maintain excellent touch sensitivity. The smooth surface ensures that touch commands are accurately registered, making it easy to swipe, tap, and interact with your device. This is crucial for smartphones and tablets, where responsiveness can greatly affect the user experience.
6. Compatibility with Additional Coatings
Many scratch-resistant glasses are compatible with extra coatings, such as oleophobic coatings that repel oil and reduce fingerprints, or anti-reflective coatings that enhance visibility under bright lighting. This versatility allows manufacturers to offer screens that not only resist scratches but also provide additional benefits, such as easy cleaning and better readability.
7. Resistance to Environmental Factors
Scratch-resistant glass is built to withstand more than just physical damage. It is also resistant to temperature changes, humidity, and exposure to chemicals, making it suitable for use in different environments. This property ensures that your device can endure various conditions without the screen degrading or becoming less effective.
8. Long-Lasting Aesthetic Appeal
Since scratch-resistant glass is designed to minimize scratches and other visible damage, it helps maintain the sleek, polished look of your device over time. This not only enhances the user’s experience but also helps preserve the resale value of the device. A smartphone with a scratch-free screen is more appealing and valuable compared to one with visible wear and tear.
9. Eco-Friendly Manufacturing Options
Modern manufacturers are increasingly focused on producing scratch-resistant glass in an environmentally responsible way. For instance, some versions of Gorilla Glass incorporate recycled materials, reducing waste and the environmental footprint of the manufacturing process. This eco-friendly approach aligns with the growing consumer demand for sustainable products.
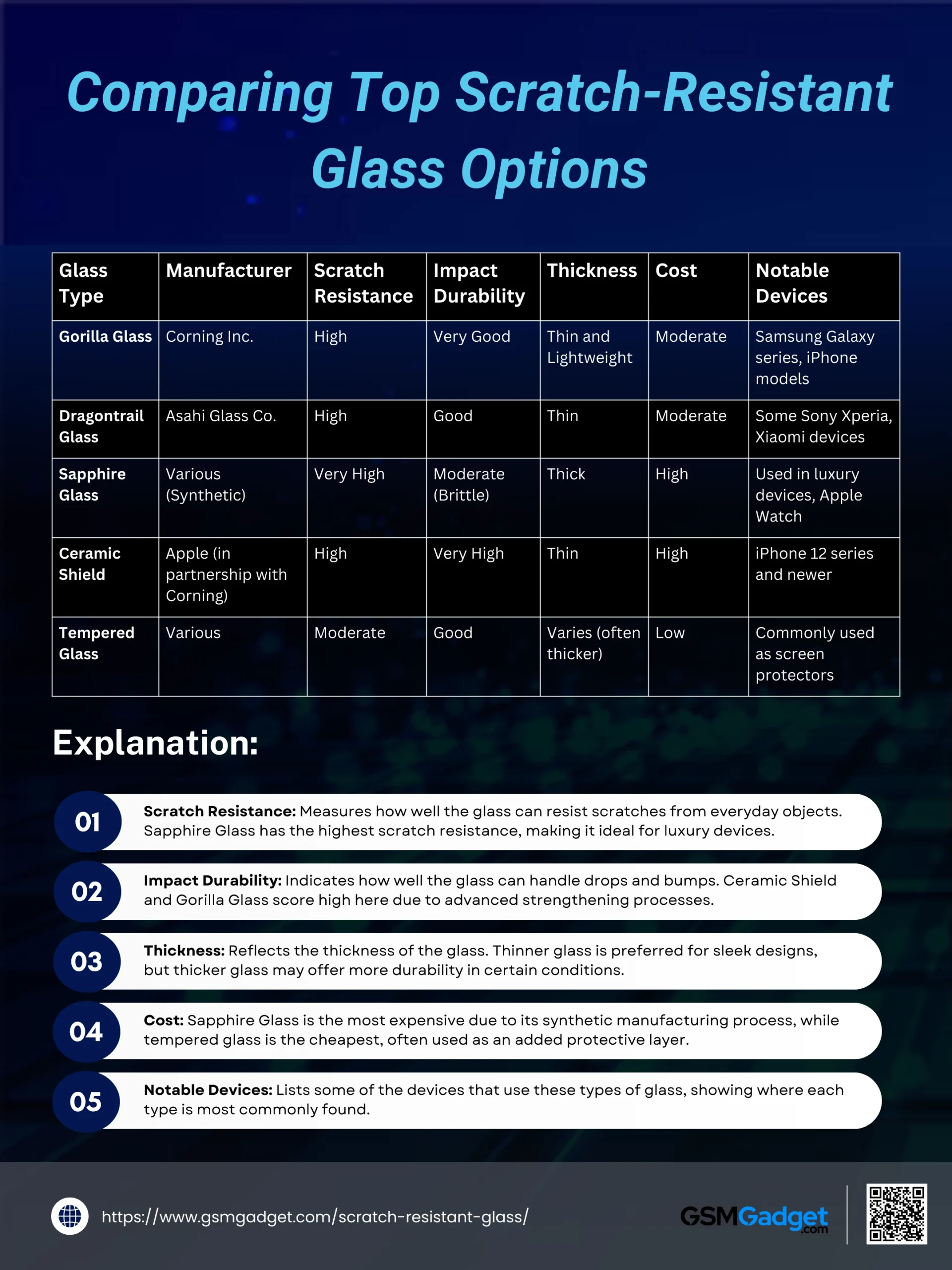 Comparing Top Scratch-Resistant Glass Options
Comparing Top Scratch-Resistant Glass Options
The table below compares these popular types of scratch-resistant glass based on their key attributes:
| Glass Type | Manufacturer | Scratch Resistance | Impact Durability | Thickness | Cost | Notable Devices |
| Gorilla Glass | Corning Inc. | High | Very Good | Thin and Lightweight | Moderate | Samsung Galaxy series, iPhone models |
| Dragontrail Glass | Asahi Glass Co. | High | Good | Thin | Moderate | Some Sony Xperia, Xiaomi devices |
| Sapphire Glass | Various (Synthetic) | Very High | Moderate (Brittle) | Thick | High | Used in luxury devices, Apple Watch |
| Ceramic Shield | Apple (in partnership with Corning) | High | Very High | Thin | High | iPhone 12 series and newer |
| Tempered Glass | Various | Moderate | Good | Varies (often thicker) | Low | Commonly used as screen protectors |
Explanation:
- Scratch Resistance: Measures how well the glass can resist scratches from everyday objects. Sapphire Glass has the highest scratch resistance, making it ideal for premium and luxury devices.
- Impact Durability: Indicates how well the glass can handle drops and bumps. Ceramic Shield and Gorilla Glass score high here due to advanced strengthening processes.
- Thickness: Reflects the thickness of the glass. Thinner glass is preferred for sleek designs, but thicker glass may offer more durability in certain conditions.
- Cost: Sapphire Glass is the most expensive due to its synthetic manufacturing process, while tempered glass is the cheapest, often used as an added protective layer.
- Notable Devices: Lists some of the devices that use these types of glass, showing where each type is most commonly found.
